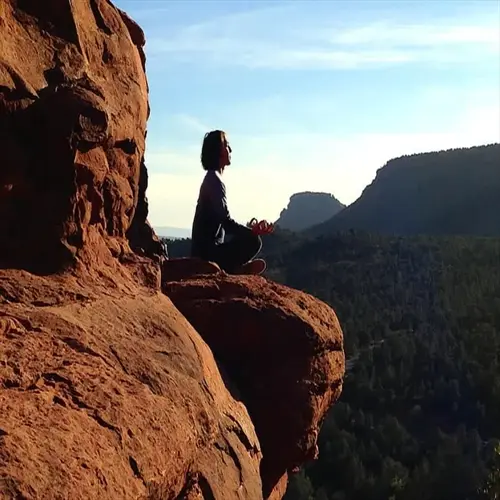
10 Essential Meditation Tips for Beginners

Written by
Chen Jialiang
Reviewed by
Prof. William Dalton, Ph.D.Begin forming the meditation habit in short, 2-minute daily sessions.
Try meditating in the morning, before distractions emerge and maintaining a regular daily session is easier.
Name it as you will, but find a comfortable seating position that avoids straining your body.
The best way to calm your racing mind with thoughts is to count your breath.
There is no judgment associated with a wandering thought - simply label it and continue returning to the present moment in awareness.
For 30 days, write down where you are up to, and do not judge what you wrote to sustain your habit.
Article Navigation
Starting with meditation tips sounds hard, but I think of my first attempts. Begin by focusing on simple breathing exercises to help calm your mind. These practices naturally reduce stress. They provide mental clarity without complicated methods. It is this method that provides beginners with immediate relief.
Meditation is best done with consistency being emphasized over attaining perfection. Do not worry about having long sessions at first. Five minutes every day is better than an hour once a week. I began sitting in meditation, only a few minutes at a time. You will gain confidence by establishing a habit.
Use meditation as a means of emotional equilibrium. Notice feelings without judgment during practice. This awareness allows a space for a response rather than a reaction. Your life is more centered. Little things add up over time.
10 Essential Meditation Tips
Starting with two minutes per day eliminates the pressure while growing your habit strength naturally. That is how I started years ago. Small wins build momentum. You don't have to feel overwhelmed. Over time, staying consistent becomes second nature.
Engage in your early day morning meditation before distractions seep in. Your mind is still fresh from sleep. Morning sessions become the foundation for your entire day. My nightly routine allows me to prepare my meditation space or put it all together in the evening. I now have a ritualized practice that ensures I won't miss my meditation.
Emphasize physical comfort rather than ideal body alignment. Use pillows or chairs that offer support. Discomfort will limit your ability to concentrate. Determine which positions feel natural. You cultivate a practice that will be sustainable.
Track progress through simple journaling without judgment. Note feelings before and after each session. Celebrate small improvements. Avoid self-criticism during your 30-day journey. This builds self-awareness gently.

Start Tiny (2 Minutes)
- Beginning with only two minutes daily makes meditation feel manageable and achievable for newcomers to the practice.
- This minimal time commitment helps establish consistency without creating pressure or resistance to starting each day.
- Gradual increases of one minute per week allow natural progression to longer sessions as confidence builds.
- Short sessions focus attention on habit formation rather than duration, making practice sustainable long-term.
- Research shows brief daily sessions yield higher adherence rates than infrequent long practices for beginners.
- The two-minute threshold removes psychological barriers, enabling effortless integration into busy morning routines.

Anchor to Morning Routine
- Practicing meditation before checking devices or starting daily activities prevents schedule conflicts and forgetfulness.
- Early morning sessions utilize fresh mental energy when willpower reserves are highest for the day.
- Creating physical reminders like sticky notes near the bed reinforces the morning meditation commitment.
- Consistent timing aligns with the body's natural circadian rhythms for enhanced focus during practice.
- Morning stillness provides quieter environments with fewer interruptions for deeper concentration potential.
- Establishing this routine first thing creates a positive tone that influences the entire day productively.

Prioritize Comfort
- Using supportive chairs or cushions prevents physical discomfort that distracts from mental focus during sessions.
- Allowing natural spinal alignment without forcing traditional postures accommodates individual physical limitations.
- Frequent position adjustments during meditation are completely acceptable to maintain comfort and attention.
- Physical ease should always take precedence over achieving picture-perfect meditation postures for beginners.
- Discomfort creates mental resistance while physical relaxation facilitates deeper states of mindful awareness naturally.
- Proper support systems prevent numbness or stiffness that could discourage continuation of regular practice.

Breathe with Numbers
- Counting inhalations and exhalations provides tangible focus points that anchor attention during meditation practice.
- The simple numerical sequence creates mental structure that naturally reduces random thought distractions.
- Resetting the count after reaching ten maintains engagement without creating performance pressure.
- This technique builds concentration stamina by giving the mind specific, manageable tasks to complete.
- Focusing on breath counting develops present-moment awareness while calming the nervous system simultaneously.
- The rhythmic pattern establishes a meditative cadence that helps synchronize body and mind effortlessly.

Label Distractions
- Naming wandering thoughts as planning or worrying creates observational distance from mental content.
- This non-judgmental categorization helps recognize thought patterns without emotional entanglement.
- Gentle mental noting maintains present-moment awareness while reducing frustration about distractions.
- Regular practice develops meta-cognition skills that transfer to daily life situations automatically.
- Identifying thought categories builds self-understanding about recurring mental habits and tendencies.
- The labeling process creates space between awareness and reactions, enhancing emotional regulation capacity.

Body Scan Daily
- Systematically moving attention from feet to head develops whole-body awareness in three-minute segments.
- Noticing physical sensations without judgment cultivates deeper mind-body connections during practice.
- Releasing discovered tension consciously teaches physical relaxation responses usable anytime.
- Regular scanning builds sensory acuity that helps detect early stress signals in daily life.
- This practice increases interoceptive awareness, improving recognition of emotional states through bodily sensations.
- Progressive scanning trains focus while promoting physical relaxation throughout the entire system simultaneously.
Guided Meditation Start
- Voice-guided sessions provide supportive structure that reduces uncertainty during initial practice attempts.
- Professional instructions model proper technique while maintaining appropriate timing and pacing.
- Varied session themes help discover personal preferences before transitioning to silent practice.
- Regular app use builds confidence through progressive skill development with expert support.
- Audio guidance prevents common beginner mistakes while introducing diverse meditation approaches safely.
- Directional support allows complete surrender to the process without decision fatigue about methods.

Loving-Kindness Phrases
- Silently repeating compassionate wishes fosters positive emotional states during meditation practice.
- Beginning with self-directed kindness builds foundational self-acceptance before extending outward.
- Gradually expanding recipients to loved ones and strangers develops emotional generosity naturally.
- Regular practice measurably increases daily feelings of connection according to research findings.
- This technique counters negative self-talk patterns while strengthening empathy and social bonds.
- Focused well-wishing rewires neural pathways associated with compassion and interpersonal connection.

Embrace Imperfection
- Accepting mental wandering as normal reduces performance anxiety about meditation effectiveness.
- Recognizing distraction as integral to practice builds patience with the learning process.
- Returning attention without self-criticism strengthens mental resilience during challenging sessions.
- This mindset transforms perceived failures into valuable training opportunities each time.
- Non-judgmental observation creates psychological safety for exploring inner experiences authentically.
- Understanding that perfection isn't required removes barriers to consistent daily meditation practice.

30-Day Commitment
- Consistent one-month practice establishes neural pathways that make meditation feel automatic.
- Brief daily journal entries track subtle progress and patterns without extensive writing.
- Fixed duration creates achievable finish line that motivates continuation beyond the trial period.
- Documenting experiences builds personal evidence of benefits that reinforce long-term practice.
- The timeframe allows noticeable psychological and physiological changes to become apparent.
- Journal reflections provide valuable insights about personal rhythms and effective techniques.
Breathing Techniques for Focus
Diaphragmatic breathing stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system. This helps calm the fight-or-flight response. Put your hands flat on your belly and your breastbone. Feel the belly come out like a balloon. This type of breathing is related to the natural slowing of the heartbeat. This can create immediate relaxation in a stressful moment.
The 4-7-8 method utilizes extended exhalation for its strongly beneficial effects. Inhale for 4 seconds, hold gently for 7 seconds, and exhale completely for 8 seconds. This pattern is ideal for promoting powerful oxygenation of the blood. It balances the carbon dioxide levels in the body. It causes the body to enter a state of deep calm.
Use box breathing to relieve acute stress: Imagine tracing a box shape. There are four equal parts: inhaling for four seconds, holding for four seconds, exhaling for four seconds and pausing for four seconds. This structure can anchor racing thoughts. I use it before all important meetings to achieve mental clarity in minutes.
You can dramatically enhance your level of concentration through the use of conscious breath control. Your prefrontal cortex receives oxygen. This brain area is responsible for focus. You build mental stamina with consistent practice. Distractions weaken. You can concentrate longer on cognitively demanding tasks.
Diaphragmatic Breathing
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly while inhaling slowly through your nose, consciously expanding your abdomen outward like a balloon filling with air for optimal oxygen intake.
- Gradually exhale through gently pursed lips while contracting abdominal muscles, ensuring each complete breath cycle lasts approximately five to six seconds for efficient gas exchange.
- Maintain focus on minimizing upper chest movement while maximizing diaphragmatic descent to stimulate the vagus nerve and reduce cortisol production throughout your body.
- Consistent five-minute daily practice strengthens respiratory muscles and enhances oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange efficiency for better overall physiological function.
- Visualize oxygen spreading through your bloodstream with each inhalation, nourishing cells and tissues while eliminating metabolic waste products systematically.
- Combine with mindful awareness of ribcage expansion to deepen the connection between breath patterns and present-moment awareness during sessions.
4-7-8 Method
- Inhale quietly through your nose for four full seconds while maintaining relaxed shoulders and an upright yet completely comfortable seated posture without tension.
- Comfortably hold the breath for seven seconds without straining, allowing oxygen saturation to reach optimal levels throughout your bloodstream and tissues.
- Exhale completely through your mouth for eight continuous seconds while making a gentle whooshing sound to regulate airflow release and lung emptying.
- Repeat this specific sequence four consecutive times to activate the body's relaxation response and measurably lower resting heart rate effectively.
- Focus on the extended exhalation phase to trigger parasympathetic nervous system dominance, creating calm mental states ideal for concentration.
- Coordinate with mental imagery of tension flowing out with each exhalation to enhance the physiological relaxation response during practice.
Box Breathing
- Inhale steadily through your nose for four controlled seconds while visualizing drawing a straight line upward along an imaginary box's left side precisely.
- Hold the breath smoothly for four seconds while mentally tracing horizontally across the top of the geometric shape without tension or physical straining.
- Exhale uniformly for four seconds while visualizing descending the box's right vertical side and maintaining consistent airflow control throughout.
- Pause comfortably for four seconds at the imagined bottom corner before initiating the next complete cycle, performing five full boxes per session.
- Use this structured approach to enhance mental focus during demanding cognitive tasks by regulating autonomic nervous system responses.
- Apply during transitions between activities to reset attention and maintain decision-making clarity throughout demanding work periods.
Resonant Breathing
- Maintain a natural pace of five complete breaths per minute to synchronize cardiac and pulmonary rhythms for optimal physiological coherence and balance.
- This specific rhythm maximizes heart rate variability, enhancing emotional regulation capabilities and stress resilience during challenging daily situations.
- Practice while sitting upright with closed eyes, focusing exclusively on smooth wave-like inhalation and exhalation patterns for five continuous minutes.
- Regular application improves autonomic nervous system balance and reduces measurable physiological stress markers over consistent practice periods.
- Coordinate with gentle rocking motions to embody the resonant rhythm physically and deepen mind-body integration during sessions.
- Notice how this breathing pattern naturally regulates blood pressure and induces states of calm focus suitable for prolonged concentration.
Pursed-Lip Breathing
- Inhale slowly through your nose for two full seconds while keeping facial muscles completely relaxed and shoulders completely tension-free throughout the process.
- Exhale gently through deliberately pursed lips for four to six continuous seconds as if blowing through a narrow straw to create therapeutic backpressure.
- This technique improves alveolar oxygen exchange efficiency while slowing respiratory rate for enhanced calm and focus during daily activities.
- Regular practice strengthens respiratory muscles and helps maintain open airways during stressful or physically demanding situations effectively.
- Apply during physical exertion to regulate breathing patterns and maintain optimal oxygen saturation levels in working muscles.
- Combine with posture awareness to maximize lung expansion and improve overall respiratory mechanics during the practice.

Morning Activation
- Begin diaphragmatic breathing immediately upon waking to stimulate blood circulation and oxygenate the brain for enhanced morning alertness and mental clarity.
- Combine deep inhalations with slow neck rotations to release muscular tension accumulated during sleep, improving cervical mobility and reducing stiffness.
- Maintain practice consistency by integrating breathing exercises with morning beverage preparation, linking the ritual to established habits for better adherence.
- Focus on abdominal expansion rather than chest movement to ensure optimal diaphragmatic engagement and maximum oxygen intake efficiency.
- Visualize oxygen flowing to extremities with each inhalation to boost cellular energy production and activate metabolic processes gently throughout your body.
- Conclude with three conscious yawns to release jaw tension and stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system for calm readiness before starting your day.

Work Focus Booster
- Implement box breathing before critical meetings to enhance concentration capabilities and improve decision-making clarity under pressure.
- Set regular hourly reminders for three-minute breathing intervals to maintain consistent oxygen flow and prevent mental fatigue accumulation.
- Combine with ergonomic posture adjustments ensuring feet are flat and spine neutrally aligned to maximize respiratory efficiency during sessions.
- Visualize work-related stress leaving your body with each extended exhalation while maintaining focus on present tasks and priorities.
- Use the breath-holding phase to mentally reset between complex tasks, creating cognitive separation and renewed attention for new challenges.
- Coordinate with brief eye exercises to reduce digital strain and integrate breath awareness into computer-based work routines seamlessly.

Evening Wind-Down
- Practice the 4-7-8 method while gradually dimming ambient lighting to naturally trigger physiological relaxation responses as bedtime approaches.
- Coordinate extended exhalations with progressive muscle relaxation sequences starting systematically from forehead down to feet for full release.
- Utilize pillow supports strategically to maintain comfortable spinal alignment while performing breathing exercises in bed before sleep.
- Focus on doubling exhalation duration compared to inhalation to strongly activate the parasympathetic nervous system dominance required for sleep.
- Pair with gratitude reflections during inhalations to cultivate positive mental states conducive to restorative sleep patterns.
- Synchronize breathing rhythms with gradual darkening of your environment to strengthen circadian rhythm alignment and sleep onset signals.

Anxiety Management
- Deploy pursed-lip breathing immediately at anxiety onset to physiologically slow respiratory rate and stabilize heart rhythm within seconds.
- Consciously extend exhalation duration longer than inhalation to trigger calming vagal nerve responses that counteract stress hormones effectively.
- Combine with tactile grounding techniques by noticing physical contact points with surfaces during practice to enhance present-moment awareness.
- Repeat breathing cycles continuously until heart rate normalizes and cognitive clarity returns to baseline functioning levels naturally.
- Visualize anxiety as a cloud dispersing with each exhalation while creating mental space for rational perspective and emotional regulation.
- Maintain gentle forward gaze to balance internal awareness with environmental connection, preventing excessive inward focus during recovery.

Pre-Sleep Routine
- Perform resonant breathing while lying in bed to synchronize cardiovascular and respiratory systems through consistent rhythmic patterns.
- Maintain a precise five-breaths-per-minute tempo to naturally induce drowsiness and prepare your physiology for efficient sleep onset mechanisms.
- Visualize bodily tension melting away progressively with each exhalation while systematically relaxing muscle groups from head to toes.
- Continue rhythmic breathing cycles until natural sleep occurs, using breath as an anchor to prevent racing thoughts and mental chatter interference.
- Coordinate with gradual body temperature reduction by removing layers during practice to align with natural thermoregulatory sleep processes.
- Integrate lavender scent inhalation during practice to associate the breathing technique with olfactory relaxation cues for conditioned response.
Creating Your Meditation Space
Focus on physical comfort above decorative appeal in your meditation area. Select supportive cushions that suit your body type and provide optimal comfort. Don't use stylish paraphernalia that can distract. I have only a simple mat and a pillow. Usability counts more than Instagrammable setups. Your practice stays concentrated.
Maintain one location for faster access to calm states of meditation. The mind associates that environment with calm. The corner of my bedroom is my meditation spot in the mornings. Nerve pathways are strengthened by repetition. After weeks, the entrance into the meditative state will become automatic.
Incorporate multi-sensory aspects such as soft lighting and textured materials. The dimmable lamps will help minimize glare and eye fatigue. Natural fiber throws help to maintain a soothing tactile experience. I have placed a small river stone to provide a focal point for touch. These cues create a deeper immersive experience while sustaining concentration.
Combat urban noise with smart adaptations. Use white noise apps or earplugs if you are living in an apartment. Heavy curtains help soften the sound of street traffic. I practice meditation in the morning during quiet hours. Minimal setups work just fine for keeping the practice going.
Seating Comfort
- Select supportive cushions or chairs allowing neutral spine alignment without straining muscles during sessions lasting up to twenty minutes.
- Test multiple options like zafus, meditation benches, or firm armchairs to find what maintains comfort without causing numbness over time.
- Ensure hips remain slightly elevated above knees when seated to promote natural spinal curvature and unrestricted breathing patterns.
Lighting Control
- Utilize adjustable light sources like dimmable lamps or blackout curtains to create soft, indirect illumination that minimizes eye strain during practice.
- Natural morning light works well for energizing sessions while warm-toned evening lighting supports relaxation-focused meditation routines.
- Avoid direct overhead lighting that creates harsh shadows and visual distraction during eyes-closed concentration exercises.
Acoustic Management
- Incorporate white noise machines or nature sound apps to mask disruptive environmental noises like traffic or household appliances during practice.
- Use acoustic panels or heavy curtains in urban environments to dampen high-frequency sounds that interrupt concentration and mental stillness.
- Experiment with comfortable earplugs for high-distraction environments while maintaining awareness of breath vibrations internally.
Personal Touches
- Add meaningful non-distracting items like smooth stones or untreated wood pieces that provide tactile grounding points during meditation sessions.
- Include one inspiring visual focus point such as a simple plant or abstract art to gently return attention when eyes are open during practice.
- Avoid cluttered decorations that compete for attention and trigger associative thinking instead of present-moment awareness.
Air Quality
- Ensure adequate ventilation with open windows or air purifiers to maintain fresh oxygen levels supporting deep breathing exercises during practice.
- Use natural essential oil diffusers sparingly with non-stimulating scents like lavender or sandalwood to create subtle olfactory anchors without overwhelming.
- Maintain comfortable humidity levels between 40-60% to prevent dry airways that can cause coughing distractions during breath-focused meditation.
Space Clearing
- Remove all non-essential items from a 3x3 foot area to create physical emptiness that supports mental decluttering during meditation sessions.
- Wipe surfaces thoroughly to eliminate dust particles that may cause allergic reactions or breathing distractions during practice.
- Evaluate energy flow by sitting in potential spots to identify areas with natural calmness and minimal electromagnetic interference.
Comfort Foundation
- Layer supportive cushions atop folded blankets to create custom elevation accommodating your hip flexibility and leg circulation needs.
- Place a non-slip yoga mat underneath seating arrangements to prevent shifting during sessions and define the practice boundary clearly.
- Adjust height until knees rest comfortably below hip level when seated cross-legged without pressure on ankle joints.
Sensory Optimization
- Position adjustable light sources at eye level when seated to provide soft illumination without creating glare or harsh shadows in the space.
- Add one natural element like a small succulent plant or river stones to provide organic textural references during tactile grounding exercises.
- Place speakers for background sounds at least three feet away to create ambient audio that doesn't overwhelm or localize attention.
Personalization
- Select a single meaningful object like a smooth worry stone to serve as a gentle visual anchor during meditation sessions without causing distraction.
- Choose neutral-colored fabrics for cushions and mats that promote calmness while avoiding stimulating patterns that might disrupt focused attention.
- Position all digital displays or reflective surfaces outside your direct line of sight to prevent accidental attention grabbing during practice.
Routine Integration
- Store meditation accessories in visible open baskets rather than closed storage to reduce setup friction and encourage daily practice consistency.
- Establish a pre-meditation ritual like lighting a specific lamp to create psychological triggers signaling transition into practice time.
- Place a small water bottle nearby to prevent dehydration disruptions without needing to leave the meditation space during sessions.
Overcoming Mental Distractions
Use *thought labels* to distance yourself from the distractions that your mind brings. When you have thoughts, you mentally categorize them as 'planning', 'worrying', etc. This noting, without judgment, reduces the intensity of such thoughts. I practice this on chaotic days. The purpose is to avoid suppressing thoughts, while still allowing focus on your breath anchor.
To rapidly restore attention, revert to sensations through the breath. Sense nostrils or belly inflating and deflating. This allows for a physical anchor to your focus, stimulating your prefrontal cortex. Increased oxygen to the attention centers then follows. If I have to write email after email, I am well-versed in this technique. In short order, the clarity of mind points accurately suggest itself.
Use the noting practice for emotional distractions. Name the feeling as 'anger' or as 'fear'. Noting feelings creates room between the stimulus and your response. I said the sensations in my body during hard conversations. You can feel the emotional intensity, but you don't need to suppress the authentic experience.
Body scanning develops interoceptive awareness to keep from drifting off. Recognize how the tension feels in your feet and then move slowly up to your head. This grounds the brain in physical reality. I often partake in body scanning when experiencing spikes in anxiety. It is effective at interrupting the obsessive thinking patterns while the spikes are happening.
Thought Labeling
- Gently name mental distractions as 'planning', 'remembering', or 'worrying' to create observational distance without judgment or emotional engagement during practice.
- This cognitive labeling technique reduces identification with thoughts while maintaining awareness of their transient nature throughout meditation sessions.
- Regular use develops meta-awareness skills that effectively transfer to daily life situations, helping recognize distraction patterns before they escalate significantly.
Breath Anchoring
- Return attention to physical breath sensations at the nostrils or abdomen whenever noticing the mind has wandered from the present moment focus.
- Counting inhalations and exhalations from one to ten provides structure while resetting reinforces the refocusing habit consistently during practice sessions.
- This somatic anchor leverages the breath's constant availability as a neutral reference point independent of thought content for reliable redirection.
Noting Practice
- Apply brief mental notes like 'hearing', 'feeling', or 'thinking' to acknowledge sensory or emotional inputs without elaboration during meditation sessions.
- This technique creates valuable space between stimuli and reactions, reducing impulsive engagement with distractions while maintaining mindful awareness.
- Regular noting cultivates equanimity by training non-reactive observation of internal and external experiences as they naturally arise and pass.
Body Scanning
- Shift attention systematically through body regions when mental chatter persists, using physical sensations as alternative anchors for present-moment focus.
- Noticing tension or temperature variations in different body parts grounds awareness in somatic reality away from abstract thought patterns.
- This technique enhances interoceptive awareness while effectively interrupting repetitive thought loops through deliberate attention redirection strategies.
Open Awareness
- Expand attention to include all sensory inputs equally without focusing on any single object when thoughts become overwhelming during sessions.
- This panoramic awareness creates spaciousness that allows distractions to arise and pass without triggering habitual engagement patterns.
- Practicing non-selective attention develops tolerance for mental noise while reducing struggle against natural thought flow over consistent practice.
Sensory Focus Drills
- Practice focusing exclusively on one sense such as sound for three minutes daily, noting distractions without engagement then returning to focus.
- Gradually increase duration while adding sensory channels to build attentional stamina and distraction resistance over consistent practice periods.
- This exercise trains selective attention control while developing awareness of automatic distraction responses effectively.
Thought Surfing
- Visualize thoughts as ocean waves during five-minute sessions, observing their rise and fall without attempting to control or suppress them consciously.
- Practice returning to breath focus whenever caught in thought undertows, reinforcing the mental muscle of redirection and refocusing.
- This metaphor reduces struggle with distractions by cultivating acceptance of thought transience through regular application.
Emotion Mapping
- When distracted by feelings, pause to identify physical sensation locations such as chest tightness before labeling the emotion specifically.
- Trace sensation changes during three complete breath cycles without analysis, allowing emotional energy to dissipate naturally over time.
- This exercise builds emotional regulation skills while disrupting habitual reaction patterns to feelings through mindful observation.
Anchor Switching
- Intentionally shift attention between three anchors including breath, sounds, and body sensations every minute during five-minute sessions.
- Notice distraction pull during transitions while practicing non-judgmental return to the current anchor point without self-criticism.
- This drill enhances cognitive flexibility while strengthening the refocusing reflex against distractions through regular repetition.
Peripheral Awareness
- Maintain breath focus while softly registering peripheral sensory information without focusing on details during meditation practice sessions.
- Expand this open monitoring gradually to include thoughts and feelings while keeping breath as primary anchor for stability.
- This exercise develops the ability to maintain focus amidst distractions without losing center through consistent training.
Building Consistency
Habit stacking helps you integrate meditation into existing routines, such as drinking coffee in the morning or brushing your teeth. This leverages existing neural circuits. I meditate immediately after I hear my alarm go off. The existing habit triggers the new habit automatically.
Micro-tracking makes the process visible. When you complete a session, mark the calendar. Little check marks create a visible reminder of your commitment. I watch my streak grow every week. This system makes you feel dedicated without feeling pressured.
Your brain creates new pathways in around 21 days. Repeated practice rewires new neural connections. Practicing meditation daily helps turn it into a habit. I felt this transformation in myself after three weeks. The habit becomes part of a 'self'.
Replace the all-or-nothing mentality with constructive re-framing. Consider missed days a way to learn from failures. Consider the cause of the failure without judging yourself. I review patterns that I can change to improve. This will help you avoid becoming discouraged and will support the long-term engagement you want.
Habit Stacking
- Anchor meditation practice to existing daily routines like morning coffee or tooth-brushing by performing it immediately before or after the established habit.
- This method leverages existing neural pathways to create automatic triggers that reduce decision fatigue and forgetfulness over time.
- Start with one consistent anchor point before adding secondary stacking opportunities throughout the day for reinforcement.
Micro-Tracking
- Record completed sessions in a visible calendar using simple symbols like checkmarks rather than detailed journal entries to minimize resistance.
- Focus on streak maintenance rather than perfection - missing one day doesn't break the chain if resumed immediately the next day.
- The visual progress display activates reward centers in the brain that reinforce the habit loop through tangible accomplishment feedback.
Time Scaling
- Begin with two-minute daily sessions and increase duration by one minute weekly only after seven consecutive days of consistent practice.
- This gradual approach prevents overwhelm while building confidence through achievable micro-goals that accommodate fluctuating daily energy levels.
- Adjust duration downward temporarily during high-stress periods rather than skipping sessions completely to maintain the habit infrastructure.
Environment Design
- Keep meditation cushions or chairs permanently visible in your practice space to reduce setup friction and serve as visual practice reminders.
- Prepare accessories like timers or blankets the night before to eliminate morning decision points that could derail consistency.
- Associate specific lighting conditions or scents exclusively with practice to create environmental triggers that prompt automatic engagement.
Accountability Systems
- Partner with a meditation buddy for daily check-ins via messaging apps to leverage social commitment for motivation during low-willpower periods.
- Join online meditation challenges with public tracking to utilize community support and healthy peer comparison as consistency drivers.
- Implement small pre-commitment devices like meditation apps with streak counters that utilize loss aversion psychology to maintain practice.
Missed Sessions
- Reset without self-judgment by performing a one-minute breathing exercise immediately upon realizing a missed session to maintain neural pathway engagement.
- Analyze the cause objectively - was it schedule conflict or motivation lapse? - then implement one preventive strategy like earlier alarms.
- Reframe the lapse as data collection rather than failure to maintain growth mindset and prevent discouragement from derailing progress.
Waning Motivation
- Reconnect with original intentions through brief journaling about desired benefits before sessions to reactivate purpose-driven motivation.
- Temporarily reduce duration to the minimum two minutes while maintaining consistency to rebuild momentum through achievable wins.
- Introduce novelty through new meditation styles or locations to stimulate interest without compromising core habit structure.
Schedule Conflicts
- Identify three alternative time slots in advance for high-activity days rather than defaulting to session cancellation when primary time is compromised.
- Keep emergency five-minute meditation options available for unexpected delays using mobile apps or audio guides requiring no preparation.
- Combine with commuting or waiting periods to transform dead time into practice opportunities without calendar adjustments.
Self-Judgment Patterns
- Practice self-compassion mantras like 'progress not perfection' before sessions to neutralize all-or-nothing thinking that undermines consistency.
- Record and review small wins weekly to build evidence against inner criticism with tangible accomplishment data.
- Separate meditation quality from consistency success - prioritize showing up regardless of perceived session effectiveness.
Plateau Effects
- Refresh practice with new techniques like walking meditation or guided visualizations to overcome automaticity that diminishes engagement over time.
- Increase duration incrementally by just thirty seconds to create manageable challenge without disrupting habit foundations.
- Attend group meditation sessions occasionally to gain fresh perspectives and observational learning opportunities from others' practices.
5 Common Myths
You must clear your mind of all thoughts completely if you want to achieve all the benefits and results of meditation.
The purpose of meditation is to increase awareness rather than to achieve complete emptiness of mind. Your mind is bound to produce thoughts while you are practicing, and the trick lies in casually observing them without any attempt to become involved before you return to your breath or chosen anchor. This non-judging observation serves to train your attention regulation or control over its activity without requiring suppression of thoughts, rendering meditation suitable even for those with busy minds. The goal is improvement in the ability to concentrate progressively rather than perfection in the accomplishment of the given aim of meditation.
Correct lotus position and rigidness of a spinal column are indispensable conditions of effective meditation practice.
Comfort of body is of more importance than classic postures in the practice of meditation. Whichever position is possible to obtain, which will produce a relaxed state of alertness, as for example, sitting in a chair, kneeling, lying down, all of which will assist in perfect meditation practice. Discomfort of body leads to lack of concentration of mind, and pillows under hips, or back rest, will tend to make the meditative condition an easy one; but it is necessary that the body rest in a position of equilibrium or poise, preventing drowsiness, but causing no fatigue or distress. With this in view, meditation is easy, the condition sought being that man, irrespective of development of morpho-physiological apparatus, shall receive the benefit of meditation practice.
Longer periods of meditation automatically give rise to more improvement than shorter and more frequent meditations.
Consistency of meditation is more important than time in meditation. Investigations have shown that the habit formed from two-minute sessions of meditation daily is more powerful than the spasmodic attempts to meditate daily for an hour. Brief daily practice forms the neural pathways of the brain quickly enough without overdoing it. After consistency ensues, longer periods of "current" meditation can be helpful. For the most part, the cumulative effect of the micro-sessions of meditation daily is greater than the marathon sessions of infrequent meditation either physiologically or psychologically.
Meditation can be viewed as an avoidance mechanism that disconnects people from real-world problems and obligations.
Meditation is not avoidance; it provides a clearer and more realistic connection with it. Training in awareness that does not react opens up space between reactions and the stimuli that provoke them, which makes possible clearer choices in difficult situations. Continued use of these tools makes emotional control possible in times of conflict, and sharpened discrimination which leads to solutions to problems. Such grounded presence has built in resilience to keep us afloat in life's problems that encroach on us without having to take them on.
Instant benefits are guaranteed in both senses: after one or two subsequent practices of meditation this is the case with all.
@The benefits of meditation, like those of physical exercise, result from it after a time, because of constant practice. Some people, indeed, feel a slight sense of calm after the first few sessions; but usually it is only after weeks of daily practice that they will find any marked effects in improved attention, emotional control, stress and anxiety, etc. Because of individual differences in neuroplasticity, the effects produced upon these various psychodynamic qualities will vary, but a number of schemes of experiment made upon different people during considerable periods of time have shown that measurable results result uniformly after a prolonged course of treatment.
Conclusion
Meditation is an evolving practice, not a finish line. Each time you practice, you evolve. I've learned this over the course of many years. Each practice brings its enlightenment. There is no perfect state to arrive at. The journey is the most important thing.
Choose self-compassion over perfection for your practice. Welcome days that your attention is back and forth. I cherish sessions that are not perfect. That kindness keeps me motivated. To judge yourself, you become resistant. Gentle persistence leads to lasting change.
Benefits come more from "consistency vs. duration". Daily two minutes can far exceed occasional marathons. Tiny habits change your brain. I'm not caught up in "but showering takes a lot of my time!". I show up. Over time, this reliability will create transformation. I become mentally rested when I commit to something for duration and consistency.
Seek to incorporate mindfulness in everyday moments. Experience your breath while in line. Experience textures in whatever you do. I find my state of calm while washing dishes. Meditation is not just about formal practice. Life becomes your sacred act.
External Sources
Frequently Asked Questions
How should beginners start meditating?
Beginners should begin with extremely short sessions of just two minutes daily. Anchor meditation to an existing morning routine before distractions begin, focus on comfortable seating positions, and use simple breath counting techniques to build foundational focus without pressure.
What are the most effective meditation techniques for newcomers?
The most accessible beginner techniques include:
- Breath counting (focusing on inhalation/exhalation cycles)
- Body scanning (systematically noticing physical sensations)
- Guided sessions (using app instructions for structure)
- Thought labeling (naming distractions without judgment)
- Loving-kindness phrases (cultivating positive intentions)
Can meditation be effectively self-taught?
Yes, meditation can be successfully self-taught using free resources like meditation apps and online tutorials. Start with foundational techniques like breath awareness, maintain consistent short daily sessions, and track progress in a journal. Many practitioners develop strong personal practices without formal instruction.
When is the optimal time to meditate?
Mornings are ideal for meditation practice due to fewer distractions and higher willpower reserves. Practice immediately upon waking before checking devices or starting daily activities. Consistency matters more than duration - establish a fixed daily time that works for your schedule.
How should one breathe during meditation?
Breathe naturally through the nose without forcing depth or rhythm. Focus on the physical sensation of breath at the nostrils or abdomen. For concentration techniques, count breaths from one to ten then restart. The key is relaxed, natural breathing that anchors attention.
What are the benefits of short meditation sessions?
Brief daily sessions build consistency more effectively than infrequent long practices. They establish neural pathways gradually, reduce psychological resistance, and fit easily into busy schedules. Even two minutes daily trains attention regulation and begins stress-response recalibration immediately.
How can one maintain meditation consistency?
Sustain consistency using these methods:
- Habit stacking (attach meditation to existing routines)
- Micro-tracking (record sessions visually)
- Accountability partnerships
- Environment design (keep cushions visible)
- Flexible duration adjustments during busy periods
Is lying down acceptable for meditation?
Yes, lying meditation is acceptable if you maintain alertness. While sitting is recommended for focus practices to prevent drowsiness, reclining positions work well for body scans or relaxation techniques. Prioritize comfort over traditional postures, especially with physical limitations.
How do I handle distractions during meditation?
Distractions are natural - acknowledge them without judgment then gently return focus. Use thought labeling techniques by mentally noting 'planning' or 'remembering'. If overwhelmed, switch anchors to physical sensations. Each refocusing strengthens attention muscles.
What defines successful meditation practice?
Success isn't thought elimination but consistent refocusing. Notice when attention wanders and gently return to your anchor. Progress appears as quicker distraction recognition, reduced self-judgment, and increased present-moment awareness during daily activities beyond formal sessions.

