Healthy Eating Benefits: A Complete Guide

Written by
David Nelson
Reviewed by
Prof. William Dalton, Ph.D.The advantages of a healthy diet include improved cardiovascular health and favorable energy levels each day
Moreover, reducing your sugar and salt intake will aid in the prevention of diabetes and hypertension
Selecting nutrient-rich foods, such as greens and berries, aids in cellular protection
Building sustainable practices through smaller and consistent changes leads to lifelong results
And lastly, myths like "carbs make you gain weight" can be dispelled when considering the science of balanced nutrition
Additionally, nourishing your body consistently with water and whole food supports your immune system and longevity systematically
Article Navigation
Knowing the benefits of healthy eating changes your viewpoint on foods. The benefits extend beyond the physical level. There are energetic benefits that give you energy and make you ready for the day. You build up your defenses against the stresses of daily life. The little changes you eventually begin to experience can lead to significant improvements in your life over time. You should start by adopting the easy change you know and particularly love. Your body will profit tremendously.
Enjoy an incredible boost of energy that lasts all day long. Whole foods give you steady energy. They do not leave you feeling sluggish like processed snacks. You notice a enhancement in mood naturally. Balanced meals help stabilize your moods. This creates a positive cycle. You feel better physically and mentally.
Prioritize lifelong health via sustainable habits. I didn't realize how profoundly my life changed when I switched from soda to infused water. Choices today determine how you will feel tomorrow. Small changes create healthy foundations. Enjoy foods that nourish you completely.
Hydration Importance
Water is your best liquid for hydrating properly. Your body needs between 1.5 and 2 liters of water per day. That's between 50 and 68 fluid ounces. This amount is necessary for functions such as transporting nutrients. Herbal teas are a great second alternative. They hydrate without added sugars.
Cut down drastically on sugar in drinks. Fruit juices should be limited to small portions. Smoothies should be based on vegetables rather than fruits. Excess sugar depletes energy and causes a midday crash. I drink cucumber water instead of sweet drinks. My mind cleared in a few days.
Adequate hydration dramatically enhances cognitive function. Your brain is more efficient. Memory recall is improved. Dehydration produces brain fog. Maintaining optimal fluid levels prevents this. In addition to energy utilization, energy maintenance depends on proper hydration. Water facilitates cellular energy production directly.
Always keep a water bottle with you. This habit has dramatically increased my energy levels. You will notice improved focus when engaging in activities. You will notice your physical stamina building. You will also see your skin glowing. Hydration has a profoundly positive impact on every system in your body.
Daily Fluid Targets
- Water should be your primary beverage throughout the day for optimal hydration without added calories
- Herbal teas contribute to hydration goals while providing antioxidant benefits and flavor variety
- Limit fruit juice and smoothies to 150ml (5 fl oz) daily to avoid excessive sugar consumption
- Alcohol dehydrates the body; balance alcoholic drinks with equal water portions for mitigation
Physiological Benefits
- Proper hydration maintains blood volume for efficient nutrient delivery to muscles and organs
- Water regulates body temperature through sweat production during physical activity or heat exposure
- Adequate fluid intake prevents joint stiffness by maintaining synovial fluid lubrication
- Hydration supports kidney function for effective waste filtration and toxin elimination processes
Cognitive Effects
- Even mild dehydration reduces concentration abilities and short-term memory retention significantly
- Fluid balance affects neurotransmitter production influencing mood stability and stress response
- Hydration optimizes oxygen flow to the brain for improved problem-solving capabilities
- Morning water intake jumpstarts neural activity after overnight fasting period
Dehydration Symptoms
- Early warning signs include persistent thirst and darker yellow urine coloration indicating concentrated waste
- Moderate dehydration causes headaches and muscle cramps due to electrolyte imbalance and reduced blood flow
- Severe cases lead to dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and confusion requiring immediate medical intervention
- Chronic low hydration contributes to fatigue and long-term kidney health complications
Hydration Tracking Methods
- Monitor urine color: pale yellow indicates proper hydration while dark yellow suggests need for more fluids
- Track daily intake using marked water bottles totaling 1.5-2 liters (50-68 fl oz) for most adults
- Weigh yourself before/after exercise; drink 500ml (17 fl oz) per 0.5kg (1 lb) weight lost during activity
- Use hydration reminder apps or smart bottles with sensors that alert when consumption falls behind targets
Reducing Sugar and Salt
Know the distinctions between *natural and added sugars*. Whole fruits, such as berries, offer fiber and vitamins. Candy is just empty calories. The *WHO basis* the recommendation of under 25 grams of added sugar daily. This is about 6 teaspoons. This daily limit will prevent energy crashes.
Control blood pressure by managing sodium intelligently. Keep sodium to fewer than 5 grams per day. That's around 1 teaspoon. Herbs like rosemary and spices like turmeric add flavor without the need for salt. I now use garlic and lemon zest instead of salt.
Instead of sugary beverages, opt for homemade flavored water, such as infused cucumber or mint water. Replace candy with frozen grapes or other frozen fruit. Look at nutrition labels for added sugars. Often, plain yogurt is a better choice than sweetened yogurt. Small changes lead to large food and health improvements over a few weeks.
Your taste buds adapt quickly. After two weeks, I no longer craved salt. Vinegar and citrus naturally brighten up dishes. Nutritional yeast adds depth to savory dishes. These substitutes will be better for your long-term heart health.

Natural Sweeteners
- Swap: Replace sugary snacks with whole fruits like berries or apples providing fiber and vitamins while satisfying sweet cravings naturally without processed sugars
- Benefit: Natural fructose digests slower than refined sugar preventing energy crashes and cravings while delivering essential antioxidants for cellular protection
- Tip: Freeze grapes for sweet frozen treats or blend bananas into creamy desserts to reduce added sugar by at least 30% per serving
- Preparation: Soak dates overnight then blend into paste for natural sweetener in baking recipes instead of white sugar
- Portion Control: Enjoy dried fruits in moderation limiting to 30g portions during meals to avoid excessive sugar intake
- Hydration Boost: Infuse water with citrus slices or mint leaves to create refreshing zero-sugar alternatives to sugary beverages
Hidden Sugar Sources
- Identify: Carefully check ingredient labels for added sugars disguised as sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup or fruit juice concentrate in unexpected products
- Limit: Condiments like ketchup contain approximately 4g sugar per tablespoon while flavored yogurts often have 15-20g added sugars per single serving container
- Alternative: Choose plain Greek yogurt and add fresh berries instead of pre-sweetened versions to reduce sugar by over 50% per serving
- Cereal Choices: Select whole-grain cereals with under 5g sugar per serving rather than frosted or honey-coated varieties exceeding 15g sugar
- Sauce Solutions: Make tomato sauce from scratch using fresh tomatoes and herbs instead of jarred versions containing added sugars
- Beverage Awareness: Recognize that sports drinks and vitamin waters often contain significant hidden sugars despite health claims

Beverage Modifications
- Reduce: Gradually decrease soda consumption as one 12oz can contains 39g sugar exceeding WHO daily recommendations in a single drink
- Flavor: Infuse water with citrus slices cucumber or mint for refreshing zero-calorie alternatives that hydrate without added sugars
- Transition: Systematically decrease sugar in tea/coffee by half teaspoon weekly to adjust taste preferences without drastic changes
- Milk Options: Choose unsweetened almond or oat milk instead of flavored varieties that contain 10-15g added sugars per cup serving
- Alcohol Moderation: Select dry wines or spirits with sugar-free mixers rather than cocktails with syrups and juices high in sugars
- Herbal Alternatives: Brew caffeine-free herbal teas like chamomile or peppermint as warming evening beverages without sugar additions

Salt Alternatives
- Enhance: Use fresh garlic lemon zest or balsamic vinegar to boost flavor complexity without sodium while adding beneficial phytochemicals
- Blend: Create custom salt-free seasoning mixes combining dried herbs like oregano basil and thyme with garlic powder for versatile flavoring
- Rinse: Thoroughly wash canned beans and vegetables under running water to remove up to 40% of added sodium before cooking
- Acidity Balance: Incorporate citrus juices or vinegar in dressings and marinades to brighten flavors reducing need for salt by enhancing natural tastes
- Umami Boost: Add nutritional yeast or mushrooms to dishes for savory depth that mimics saltiness without sodium content
- Texture Contrast: Include crunchy elements like toasted nuts or seeds to provide sensory satisfaction that reduces salt cravings

Cooking Techniques
- Prepare: Cook meals from scratch using whole ingredients to control sodium content rather than relying on processed foods high in salt
- Season: Add salt at end of cooking process to maximize surface flavor perception while using significantly less quantity overall
- Roast: Enhance natural sweetness of vegetables through caramelization at high heat creating depth without needing added salt or sugars
- Broth Basics: Make homemade vegetable broth without salt instead of using store-bought versions containing 600-800mg sodium per cup
- Marinade Magic: Use citrus juices vinegars and herbs in marinades to tenderize proteins and infuse flavor without salty brines
- Slow Cooking: Develop complex flavors through extended low-temperature cooking that builds richness naturally reducing need for salt

Snack Solutions
- Nut Choices: Select unsalted raw or roasted nuts providing healthy fats and protein without added sodium or sugary coatings
- Veggie Prep: Keep pre-cut vegetables like bell peppers and cucumbers ready for quick snacks with hummus instead of salty chips
- Yogurt Options: Combine plain Greek yogurt with cinnamon and apple slices rather than sweetened yogurts with candy mix-ins
- Popcorn Prep: Air-pop popcorn then season with nutritional yeast or herbs instead of microwave bags high in salt and trans fats
- Trail Mix: Create custom mixes with unsweetened dried fruits and raw seeds avoiding salted nuts and candy-coated additions
- Dipping Alternatives: Use mashed avocado or Greek yogurt dips seasoned with herbs instead of pre-made salty dips and spreads

Dining Out Strategies
- Request: Ask for dressings and sauces on the side to control sodium and sugar intake while still enjoying flavors moderately
- Swap: Substitute french fries or chips with steamed vegetables or side salad without high-sodium dressings or toppings
- Preparation: Choose grilled baked or steamed options rather than fried foods that often contain both added salt and sugars
- Broth Awareness: Select clear soups over creamy versions which typically contain less sodium and avoid sugary glazes on proteins
- Portion Control: Share desserts or choose fruit-based options to satisfy sweet cravings without excessive sugar consumption
- Beverage Choice: Order sparkling water with lime instead of sugary sodas or alcoholic cocktails when dining out
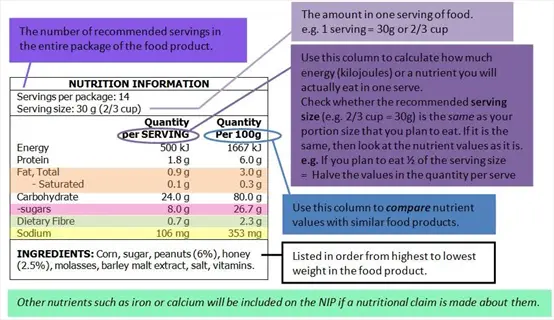
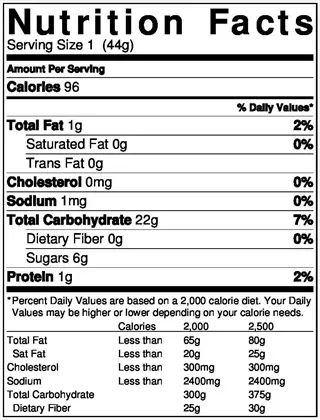
Label Literacy
- Terminology: Recognize that 'sodium-free' means less than 5mg per serving while 'low sodium' indicates under 140mg per serving
- Sugar Aliases: Identify hidden sugars listed as dextrose maltose sucrose or fruit juice concentrates on ingredient labels
- Daily Values: Use percentage daily value with 5% or less considered low for sodium and added sugars per serving size
- Serving Awareness: Check actual serving sizes versus package contents as some products list unrealistically small portions
- Comparison: Evaluate similar products side-by-side selecting options with lowest sodium and sugar values per 100g
- Front Claims: Verify 'reduced sugar' or 'low sodium' claims by checking nutrition facts panel for actual numbers

Breakfast Modifications
- Cereal Switch: Choose oatmeal or unsweetened whole-grain cereals topping with fresh fruit instead of pre-sweetened varieties
- Yogurt Upgrade: Mix plain yogurt with chia seeds and berries rather than flavored yogurts containing 15-20g added sugars
- Toast Toppings: Spread mashed avocado or nut butter on whole-grain toast instead of sugary jams or chocolate spreads
- Smoothie Control: Blend vegetables protein and limited fruit without adding honey syrups or sweetened juices
- Baked Goods: Make muffins with mashed banana or applesauce as natural sweeteners reducing added sugars by half
- Beverage Choice: Drink plain coffee or tea without sugar rather than sweetened coffee drinks exceeding daily limits
Long-Term Adaptation
- Taste Adjustment: Allow 2-4 weeks for taste buds to adapt to lower sugar and salt levels as sensitivity naturally increases
- Progressive Reduction: Decrease sugar in recipes by 10% weekly and salt by ¼ teaspoon increments for sustainable change
- Flavor Exploration: Experiment with global spice blends like za'atar or garam masala to discover new flavor dimensions
- Hydration Support: Drink adequate water throughout the day to help reduce cravings for salty and sweet foods naturally
- Mindful Eating: Practice attentive tasting focusing on natural flavors without distractions to appreciate subtle tastes
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate non-scale victories like improved energy levels rather than focusing solely on restrictions
Choosing Nutrient-Dense Foods
Choose foods that have the best nutrient density per WHO standards. The optimum in vitamins and minerals per calorie are these foods. Leafy greens such as spinach and kale are good examples. Berries and colored peppers are also rich in powerful antioxidants.
For maximum benefits, eat a rainbow of colorful produce. Specific colors mean different phytonutrients. For example, red tomatoes offer lycopene, orange carrots provide beta-carotene, and purple cabbage has anthocyanins. This diversity helps your body defend itself naturally.
Visually compare wholesome foods to processed foods. The colorful, fresh products are vibrant. The packaged products are colorless. Choose fresh, crunchy apples over sweetened cereals. Select wholesome lentils as a healthier alternative to canned soups. Select a wonderful variety of colors on your plate.
Discover nutrient sources without breaking the bank. Seasonal vegetables are inexpensive. Frozen berries are a good choice year-round. Purchasing in bulk is wise for whole grains. Beans and eggs are a cost-effective source of protein. I keep these items in mind when planning inexpensive meals.
Vegetables and Legumes
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale and Swiss chard provide iron, calcium and vitamins A/C/K per calorie
- Colorful Vegetables: Bell peppers, carrots and beets offer carotenoids and antioxidants supporting cellular health
- Cruciferous Options: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower contain sulforaphane with cancer-protective properties
- Legume Power: Lentils, chickpeas and black beans deliver plant protein, fiber and minerals like magnesium and zinc
- Allium Family: Garlic and onions supply allicin compounds with antimicrobial and cardiovascular benefits
- Sea Vegetables: Seaweed varieties like nori provide iodine essential for thyroid hormone production
Fruit Selection
- Berry Benefits: Blueberries, strawberries and raspberries provide anthocyanins for cognitive protection
- Citrus Choices: Oranges, grapefruits and lemons offer vitamin C and flavonoids enhancing immunity
- Tropical Varieties: Papaya, pineapple and mango supply digestive enzymes and vitamin A precursors
- Stone Fruits: Apricots, peaches and plums contribute potassium and carotenoids for skin health
- Melon Options: Watermelon and cantaloupe deliver hydration plus lycopene/carotenoids for UV protection
- Apple Advantages: Apples with skin provide quercetin and pectin for heart health and digestion
Whole Grains
- Ancient Grains: Quinoa, amaranth and teff provide complete protein and magnesium
- Oat Advantages: Steel-cut oats offer beta-glucan fiber reducing LDL cholesterol levels
- Whole Wheat: Choose 100% whole-grain breads and pastas retaining B vitamins and minerals
- Pseudocereals: Buckwheat and wild rice deliver antioxidants absent in refined grains
- Barley Benefits: Hulled barley contains beta-glucans and selenium for immune support
- Millet Nutrition: This gluten-free grain provides magnesium and phosphorus for bone health
Lean Proteins
- Plant Proteins: Tofu, tempeh and edamame provide isoflavones supporting hormonal balance
- Poultry Selections: Skinless chicken and turkey breast offer high-quality protein with minimal saturated fat
- Fish Choices: Salmon, mackerel and sardines supply omega-3 fatty acids EPA/DHA for heart health
- Egg Nutrition: Whole eggs contain choline for brain function and lutein for eye health
- Shellfish Options: Shrimp and scallops provide zinc and copper for enzyme functions
- Game Meats: Lean bison and venison offer iron and B12 with less saturated fat than beef
Healthy Fats
- Plant Oils: Olive, avocado and walnut oils provide monounsaturated fats and polyphenols
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia and flaxseeds offer fiber, vitamin E and essential fatty acids
- Avocado Benefits: Creamy texture supplies potassium and glutathione for detoxification
- Fatty Fish: Herring and trout deliver vitamin D alongside anti-inflammatory omega-3s
- Coconut Products: Unsweetened coconut provides medium-chain triglycerides for energy metabolism
- Seed Butters: Tahini and sunflower seed butter supply minerals like selenium and magnesium
10 Key Benefits of Healthy Eating
Heart health benefits from soluble fiber, which binds cholesterol. Blood pressure is controlled by potassium. Eat oatmeal every day. Include berries for antioxidants. These small choices help protect your arteries over time. Your cardiovascular system grows stronger with each meal.
Consider antioxidants your cellular bodyguards that protect your cells from damage. Vibrantly colored vegetables such as bell peppers reduce inflammation. I consume carrots and hummus as a snack. Within weeks, I noticed a significant difference in the response of my immune system due to this simple habit.
Digestive health is cultivated through the consumption of fiber-rich foods. Foods like beans and whole grains support the growth of healthy gut bacteria. You may try adding lentils to soups, for example. Your microbiome naturally improves digestion. You can stabilize your energy level with no more sugar highs and crashes.
Lasting bone strength develops through a lifetime of eating calcium-rich foods. Foods high in calcium include collard greens and sardines, so be sure to incorporate them into your weekly diet. Over time, this will reduce your risk of fractures. Your skeleton will remain strong as you age.
Enhanced Heart Health
- Mechanism: Soluble fiber binds cholesterol while potassium regulates blood pressure
- Foods: Oats, beans, bananas, leafy greens, and fatty fish like salmon
- Impact: Reduces LDL cholesterol by 10-15% and lowers hypertension risk
- Example: Daily oatmeal breakfast with berries improves arterial flexibility
- Long-term: Cumulative effect decreases heart attack and stroke likelihood
Effective Weight Management
- Mechanism: High-fiber foods increase satiety hormones and slow digestion
- Foods: Whole grains, legumes, apples with skin, chia seeds, and broccoli
- Impact: Supports calorie reduction without conscious restriction
- Example: Snacking on almonds instead of chips reduces daily calorie intake
- Long-term: Maintains healthy BMI reducing obesity-related disease risks
Improved Mood Stability
- Mechanism: Omega-3s build brain cell membranes and regulate neurotransmitters
- Foods: Walnuts, flaxseeds, avocados, and cold-water fish like mackerel
- Impact: Supports serotonin production and emotional balance
- Example: Mediterranean diet patterns correlate with positive mood outcomes
- Long-term: Consistent nutrient intake prevents mood swings and anxiety
Stronger Bones and Teeth
- Mechanism: Calcium and vitamin D synergize for mineral absorption and retention
- Foods: Collard greens, sardines, fortified plant milks, and sesame seeds
- Impact: Increases bone mineral density reducing fracture risks
- Example: Daily calcium-rich foods equivalent to 3 cups of kale or broccoli
- Long-term: Prevents osteoporosis and maintains dental integrity lifelong
Reduced Cancer Risks
- Mechanism: Phytochemicals neutralize free radicals and repair DNA damage
- Foods: Berries, cruciferous vegetables, garlic, green tea, and turmeric
- Impact: Certain compounds block tumor growth signaling pathways
- Example: Sulforaphane in broccoli sprouts inhibits breast cancer cell growth
- Long-term: Cumulative antioxidant protection lowers cellular mutation rates
Optimized Digestion
- Mechanism: Fiber adds bulk while probiotics balance gut microbiome
- Foods: Fermented foods (kimchi, kefir), whole grains, and Jerusalem artichokes
- Impact: Supports regularity and reduces digestive discomfort
- Example: Daily 30g fiber intake from diverse sources ensures healthy digestion
- Long-term: Maintains gut lining integrity preventing leaky gut syndrome
Sustained Energy Levels
- Mechanism: Complex carbs provide gradual glucose release avoiding spikes
- Foods: Sweet potatoes, quinoa, lentils, and steel-cut oats
- Impact: Prevents midday crashes maintaining focus for extended periods
- Example: Bean-based lunch sustains energy better than refined carb meals
- Long-term: Stabilizes blood sugar reducing diabetes development risk
Better Sleep Quality
- Mechanism: Magnesium relaxes muscles while tryptophan converts to melatonin
- Foods: Pumpkin seeds, spinach, turkey, and tart cherries
- Impact: Supports longer deep sleep duration
- Example: Magnesium-rich snack before bed reduces nighttime awakenings
- Long-term: Consistent sleep patterns enhance cellular repair processes
Enhanced Immunity
- Mechanism: Vitamins A/C/D and zinc boost white blood cell production
- Foods: Citrus fruits, bell peppers, mushrooms, and sunflower seeds
- Impact: Strengthens immune response against common illnesses
- Example: Daily vitamin C from 1 orange + 1 bell pepper supports immune function
- Long-term: Strengthens adaptive immunity for pathogen recognition memory
Increased Longevity
- Mechanism: Polyphenols activate longevity genes and reduce inflammation
- Foods: Extra virgin olive oil, dark chocolate, berries, and green tea
- Impact: Supports cellular health and functional aging
- Example: Blueberry consumption correlates with delayed cognitive decline
- Long-term: Combined effects delay age-related functional decline
Sustainable Healthy Habits
Create sustainable habits with small changes. Each day, add 1 vegetable to your breakfast. Drink water when your coffee percolates. These micro-actions build on one another. I started by keeping fresh fruit on my counter. This simple adjustment helped improve my snacking habits.
Habit stacking piggybacks on things we do already. Tying new actions to established activities you do is the answer. After brushing your teeth, pack lunch for the following day. Before going grocery shopping, eat a small meal. The tying of these activities allows the habit to take root. I tied my phone calls to my afternoon walks.
Change your environment for success. In the refrigerator, place cut vegetables at eye level and store processed snacks out of sight. Use smaller plates automatically. I changed my kitchen to make better choices every day.
Select non-food rewards regularly. Enjoy the extra energy with a nice bath. New workout clothes may mark a new chapter in your life. Document clearer skin with before-and-after photographs. These recognitions reinforce constructive behaviors. I reward consistency with nature walks.
Gradual Implementation
- Start Small: Begin with one change weekly like adding vegetables to breakfast
- Progression: Increase water intake by one glass daily until reaching 6-8 glasses
- Sugar Reduction: Cut sweetener amounts by half each week in coffee/tea
- Salt Adaptation: Reduce salt in cooking by ¼ teaspoon weekly for palate adjustment
- Portion Control: Use smaller plates first, then focus on balanced portions later
Environmental Optimization
- Visibility: Keep fruit bowl on counter and hide unhealthy snacks out of sight
- Preparation: Wash/chop vegetables immediately after grocery shopping for easy access
- Portion Packaging: Pre-portion nuts/seeds into small containers for grab-and-go snacks
- Meal Prep: Cook grains and proteins in bulk for quick meal assembly during busy days
- Water Accessibility: Keep filled water bottles in key locations (desk, car, bedside)
Habit Stacking Techniques
- Morning Routine: Drink water while waiting for coffee to brew
- Mealtime Habit: Add vegetables to omelets or sandwiches routinely
- Post-Meal: Brush teeth after dinner to reduce nighttime snacking
- Grocery Habit: Always start in produce section before shopping other aisles
- Cooking Routine: Prepare extra vegetables to add to next day's lunch
Mindset and Motivation
- Non-Scale Wins: Celebrate improved energy, better sleep or clearer skin
- Flexible Approach: Allow occasional treats without guilt to prevent bingeing
- Progress Tracking: Use simple habit trackers rather than calorie counting
- Social Support: Join communities with similar health goals for accountability
- Self-Compassion: View slip-ups as learning opportunities, not failures
Budget-Friendly Nutrition
- Seasonal Buying: Purchase produce in season for peak nutrition and lower cost
- Frozen Options: Use frozen fruits/vegetables which retain nutrients at lower prices
- Plant Proteins: Incorporate beans and lentils as affordable meat alternatives
- Bulk Purchasing: Buy whole grains and nuts in bulk for cost savings
- Leftover Creativity: Repurpose dinner components into next-day lunches
5 Common Myths
To lose weight and protect your heart, you must eliminate fat from all your food.
This error neglects the importance of healthy unsaturated fats in the diet, which are found in foods such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, which reduce LDL cholesterol and inflammation. Healthful fats supply essential fatty acids that support brain function, hormone production, and vitamin absorption, and promote satisfaction that prevents overeating. Substituting healthy fats for refined carbohydrates often increases metabolic health indices.
Carbohydrates inherently cause weight gain and should be eliminated from diets.
This oversimplification ignores the crucial difference between refined carbs like white bread and nutrient-dense whole grains such as quinoa and oats. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, essential B vitamins, and fiber that regulates digestion. Balanced intake supports metabolic health while extreme restriction can trigger fatigue, nutrient deficiencies, and unsustainable eating patterns.
Nutrients can't be replaced with supplements.
Nutritional supplements can help with specific nutrient deficiencies, but they lack the combination of phytochemicals, fiber, minerals and vitamins that are naturally found in whole foods. Many plant substances working together cannot be replaced either by diet or by individual substances. Whole foods have nutritional advantages over supplements in absorption and digestion that pills cannot equal.
Eating healthfully requires considerable expense for special foods that must be constantly prepared.
Nutritious eating can also be accomplished with inexpensive seasonal fruits, frozen vegetables, bulk grain products and vegetable proteins, such as lentils. Simple cooking methods, e.g. roasting, require a minimum of preparation time. Batch cooking and sensible use of left-overs make it easier than is often thought to eat healthful food.
Juice cleanses effectively detoxify the body and reset metabolism.
The human liver and kidneys naturally detoxify the body without extreme interventions. Juice cleanses often lack protein and fiber while flooding the system with sugar. Sustainable health comes from consistently eating balanced meals with vegetables, proteins, and healthy fats rather than restrictive short-term protocols that often backfire metabolically.
Conclusion
Little, steady adjustments of some kind produce great effects in time. Each daily choice leads to lasting improvements in health. I started eating just one extra dish of vegetables per day. That modest habit led to a lifetime of continued good health. Learn to trust the method of gradual progress.
Select adaptable options that work for your life. There really won't be a best or perfect plan. Consider your tastes and schedule. Consider the benefits associated with stable energy levels and mood. Those advancements are the results of personalized nutrition models.
Take a look at those gains in heart health and immune function as we've been discussing. They will become your reality as long as you take consistent action. Start today, even with one tiny move. Replace soda with herbal tea. Add vegetables to your lunch plate.
Your first action begins now. Select one change from this guide. Implement it in the morning. Notice how your body reacts positively. This will propel you. Health transformation begins with a single change.
External Sources
Frequently Asked Questions
How does healthy eating benefit your body long-term?
Consistent healthy eating reduces chronic disease risks while enhancing daily energy and mental clarity. Key advantages include:
- Improved cardiovascular function through better cholesterol management
- Enhanced cognitive performance and mood stability
- Stronger immunity against common illnesses
- Slower cellular aging processes
Can healthy eating improve emotional well-being?
Yes, nutrient-dense foods directly influence neurotransmitter production. Omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins regulate serotonin levels, while stable blood sugar prevents mood crashes. This creates sustained emotional balance and reduces anxiety symptoms over time.
What happens when you transition to healthy eating?
Initial changes include stabilized energy levels and reduced cravings. Digestive regularity improves within days, followed by better sleep quality. Long-term benefits like enhanced immunity and mental clarity develop over consistent practice.
How does hydration impact overall health?
Proper hydration facilitates essential bodily functions:
- Maintains blood volume for nutrient delivery
- Regulates body temperature through sweat
- Supports kidney filtration of toxins
- Prevents joint stiffness via synovial fluid
- Enhances cognitive focus and memory retention
Do healthy eating habits affect longevity?
Yes, nutrient-rich diets activate cellular repair mechanisms. Antioxidants in colorful produce reduce oxidative stress, while omega-3s decrease inflammation. Combined with stable blood sugar control, these factors significantly extend healthspan and lifespan.
Can dietary changes improve skin appearance?
Absolutely. Hydration plumps skin cells while vitamins C and E boost collagen production. Zinc and selenium reduce inflammation causing acne. Healthy fats maintain skin elasticity, creating visible radiance within weeks.
What are sustainable ways to start eating healthier?
Effective approaches include:
- Swap one processed snack daily for whole foods
- Use smaller plates to control portions effortlessly
- Pre-chop vegetables for quick access
- Attach new habits to existing routines
- Celebrate non-scale victories like energy boosts
Is avoiding all fats necessary for health?
No, this common myth is misleading. Unsaturated fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil actually reduce inflammation and support brain function. The key is replacing trans fats with these beneficial alternatives.
How does sugar reduction impact the body?
Lowering sugar intake stabilizes insulin response, preventing energy crashes. It reduces fatty liver disease risk and supports healthy gut bacteria. Visible benefits include weight management and reduced chronic inflammation markers.
Why prioritize nutrient-dense foods?
Nutrient-dense options deliver maximum vitamins and minerals per calorie. Foods like leafy greens, berries, and lean proteins provide antioxidants, fiber, and essential fatty acids that processed alternatives lack. This optimizes cellular function efficiently.

