Meditation for Anxiety: Your Complete Guide

Written by
Leilani Ibeh
Reviewed by
Prof. William Dalton, Ph.D.Physically, meditation lessens amygdala reactivity to triggers of stress.
Short sessions done repeatedly over time lower cortisol levels more effectively than doing longer sessions occasionally.
Those who meditate every day will train their brains to respond to stress with an ever-automatic state of calm, by way of new neural pathways over time.
Using techniques such as 4-7-8 breathing can relieve anxiety in the moment when a person is in a crisis.
Meditation interrupts anxiety- tension cycles through body awareness practices.
The beginner meditator will experience noticeable reductions in anxiety within weeks of practicing regularly on a daily basis.
Article Navigation
Every day, countless millions physically and mentally suffer from anxiety. The heart quickens. Thoughts race. Meditation for anxiety offers a scientifically proven answer to this problem in a manner that alters your brain. Studies have shown that it alters the brain's structure. Such changes reduce the body's stress responses. They allow us to regain control over ourselves.
This guide makes meditation practical for everyone. You need no experience. The techniques work whether you are new to meditation or have experience. They will help you rewire the way your brain operates. You will learn easy methods that you can handle. Feel calm already!
How Meditation Helps Anxiety
Your brain has a part called the amygdala, which is an over-sensitive alarm system for anxiety that repeatedly sets off false alarms. Meditation allows you to reprogram this system. The body no longer responds to daily stress in the same way it does to emergencies. The state of constant alertness begins to subside.
Meditation reduces cortisol levels considerably. You're going to see and feel physical changes right away. Your shoulders loosen. Your breathing slows. Tension headaches lessen. These changes occur because your body's production of stress hormones is reduced when meditating.
Your heart rate naturally slows when you meditate. Before you practice, it is quite often 75, but after you have been doing it regularly, it settles down at a soothing 68. This physiological calmness helps to check the cycle of anxiety.
Another significant advantage is the reduction of mental rumination. Those racing thoughts that keep you up at night start to quiet. You begin to fall asleep quickly. Your sleep will feel deeper. Waking refreshed turns from a rarity to a normal occurrence.
Amygdala Calming
- Fact: Meditation reduces amygdala volume significantly after consistent practice, decreasing fear responses. Brain imaging shows observable structural changes in regular meditators.
- Fact: The amygdala triggers fight-or-flight reactions during perceived threats. Meditation weakens this pathway, helping you respond calmly to stressors instead of reacting anxiously.
- Fact: Daily practice lowers amygdala activation over time, making you less reactive to anxiety triggers. This effect persists during stressful situations.

Cortisol Reduction
- Fact: Meditation lowers cortisol levels in chronic anxiety sufferers. Biomarker analysis indicates consistent decreases after regular practice sessions.
- Fact: High cortisol causes physical anxiety symptoms like rapid heartbeat and muscle tension. Meditation breaks this cycle by activating the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Fact: Lower cortisol levels improve immune function and reduce inflammation markers. This creates a positive feedback loop for better overall health.
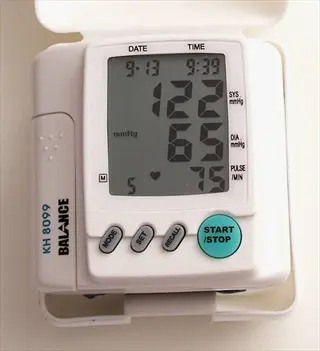
Blood Pressure Control
- Fact: Systolic blood pressure drops noticeably in hypertensive patients who meditate daily. This reduction equals some interventions without side effects.
- Fact: Meditation improves blood vessel elasticity and reduces arterial stiffness. Better circulation means reduced physical anxiety symptoms like cold hands.
- Fact: Consistent practice helps maintain healthy blood pressure during stressful events. The body learns to return to baseline faster after adrenaline spikes.

Muscle Tension Release
- Fact: Muscle tension decreases faster during meditation than passive rest. Measurements show significant reduction in trapezius and neck muscle activity.
- Fact: Chronic muscle tension worsens anxiety through pain feedback loops. Meditation interrupts this cycle by increasing body awareness and relaxation.
- Fact: Short body scan meditation reduces physical discomfort substantially. The effect lasts several hours post-practice.

Rumination Reduction
- Fact: Worry time decreases noticeably after mindfulness meditation. People report fewer intrusive thoughts and shorter worry episodes.
- Fact: Meditation creates cognitive distance from anxious thoughts. Practitioners learn to observe worries without emotional entanglement, reducing their impact.
- Fact: Brain wave measurements show decreased active thinking patterns and increased calm awareness during and after meditation.

Sleep Improvement
- Fact: Sleep quality improves in insomniacs after consistent meditation. Participants fall asleep faster and wake less frequently at night.
- Fact: Meditation supports melatonin production while decreasing cortisol at bedtime. This creates optimal biochemical conditions for restful sleep.
- Fact: Deep sleep duration extends in regular practitioners. More restorative sleep improves next-day anxiety resilience.
Heart Rate Regulation
- Fact: Resting heart rate decreases after meditation practice. This indicates improved cardiovascular efficiency and lower stress load.
- Fact: Heart rate variability increases significantly, showing better nervous system balance. Higher variability correlates with reduced anxiety sensitivity.
- Fact: During panic attacks, meditation-trained individuals recover baseline heart rate faster through breath control techniques.

Emotional Resilience
- Fact: Meditation affects the prefrontal cortex region that governs emotional regulation and decision-making.
- Fact: Practitioners show faster recovery from upsetting events. Reduced emotional reactivity to negative stimuli is observable.
- Fact: Daily meditation builds cognitive flexibility, helping reframe anxious thoughts. This skill transfers to real-life stressful situations.

Breathing Efficiency
- Fact: Respiratory rate decreases during meditation. Slower breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Fact: Oxygen consumption drops during practice, indicating deep metabolic rest. This state counteracts anxiety's physiological burden.
- Fact: Trained meditators maintain calm breathing patterns during stress, preventing hyperventilation and panic symptoms.

Focus Enhancement
- Fact: Attention span increases after mindfulness practice. People show improved performance on concentration tests.
- Fact: Meditation reduces mind-wandering in anxiety sufferers. Fewer distracting thoughts means less fuel for anxious spirals.
- Fact: The attention control center shows increased activity in meditators, helping redirect focus from worries.
Essential Techniques for Beginners
The mindfulness meditation practice develops your ability to pay attention to the present moment. There is a two-fold approach: Think about your breath without judging your thoughts.Feel the incoming air in your nostrils.Sense your rib cage rising and dropping.Watch your thoughts coming up and gently acknowledge what they are, and then focus back on breathing.
Practice progressive muscle relaxation to ease tension throughout your body. Begin with your toes. Tense them for five seconds and then completely release. Slowly continue this process up through your legs and feet, abdomen, arms, and shoulders. Notice the feeling of warmth and relaxation spreading through each muscle area after you have released the tension.
When you feel an increase in anxiety, use 4-7-8 breathing. Inhale quietly through your nose for four counts. Hold at the top for seven seconds. Exhale completely through pursed lips for eight counts. Do this three times. It will quickly calm your nervous system.
Guided meditations are a good option for beginners. You listen to the recorded directions that lead you through visualizations. You focus on the voice of the person and the images they ask you to create. This level of structure helps support individuals who find silent meditation challenging at first.
Mindfulness Meditation
- Technique: Sit comfortably and focus attention on natural breathing rhythm. Notice thoughts without judgment and gently return focus to breath.
- Benefit: Builds present-moment awareness that interrupts anxiety thought cycles. Creates mental space between you and anxious feelings.
- Tip: Start with 5-minute sessions. Use breath as anchor when mind wanders to worries.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
- Technique: Tense muscle groups for 5 seconds then release completely. Move systematically from toes to forehead, noticing tension release.
- Benefit: Breaks physical anxiety feedback loops. Reduces muscle tension contributing to stress symptoms.
- Tip: Pair with visualization: imagine stress melting away with each release. Use before sleep for tension relief.
Breath Awareness
- Technique: Practice 4-7-8 breathing: inhale 4 seconds, hold 7 seconds, exhale 8 seconds. Maintain smooth, controlled breathing pattern.
- Benefit: Activates parasympathetic nervous system quickly. Slows heart rate during acute anxiety within 90 seconds.
- Tip: Place hand on belly to feel diaphragmatic breathing. Use during stressful moments as portable calm tool.
4-7-8 Breathing
- Technique: Practice 4-7-8 breathing: inhale 4 seconds, hold 7 seconds, exhale 8 seconds. Maintain smooth, controlled breathing pattern.
- Benefit: Activates parasympathetic nervous system quickly. Slows heart rate during acute anxiety within 90 seconds.
- Tip: Place hand on belly to feel diaphragmatic breathing. Use during stressful moments as portable calm tool.
Guided Meditation
- Technique: Follow audio instructions that lead through visualization or body awareness exercises. Focus on the guide's voice and suggested imagery.
- Benefit: Provides structure for beginners struggling with silent practice. Reduces mental effort during anxious states.
- Tip: Use apps or online resources. Start with 10-minute sessions before progressing to longer practices.
Body Scan Meditation
- Technique: Mentally scan body parts sequentially, noticing physical sensations without judgment. Start at toes and move slowly upward.
- Benefit: Increases body awareness and interrupts pain-tension-anxiety cycles. Grounds attention in present physical reality.
- Tip: Practice lying down initially. Notice temperature, tingling, or pressure without trying to change anything.
Step By Step 7-Day Routine
Prepare your surroundings before you begin. Sit comfortably with your back straight. Place your feet flat on the floor. Pick a quiet area. Low light can help with concentrating. Feel the cool air that enters your nostrils while doing breathing exercises. Feel the texture beneath you.
On the first day, begin with progressive muscle relaxation. Contract and relax the muscles in an orderly fashion. Start with the toes of the feet and go up slowly. If you experience discomfort while sitting, lie down. Use the pillows for support. Observe the feeling of warmth and comfort in the lower limbs after the tension is released.
Shift to practicing breathing methods mid-week. Practice 4 7 8 breathing. Notice your abdomen rise with every inhale. Silently count. If anxiety arises, observe it non-judgmentally. Draw focus back to breath. This gradually builds mental resilience.
Conclude with guided meditation. Headphones provide an immersive atmosphere. Follow the instructions of the voice. You might visualize something calming. Perhaps you're distracted; you notice it passively. You can change positions at any time. Standing can work when sitting becomes confining. Consistency is more important than perfection.
Day 1: Progressive Muscle Relaxation
- Setup: Lie flat with arms at sides. Keep eyes closed throughout.
- Steps: Tense feet for 5 seconds → release. Notice warmth spreading. Move to calves → thighs → abdomen → hands → arms → shoulders → face. Complete sequence takes 5 minutes.
- Focus: Physical tension release. Visualize stress melting away with each muscle group.
- Modification: If lying uncomfortable, sit upright and focus on upper body.
Day 2: Progressive Muscle Relaxation
- Setup: Same position as Day 1. Add soft background nature sounds if helpful.
- Steps: Repeat full-body sequence. Spend extra time on tense areas. After releasing, count 10 breaths focusing on residual warmth in muscles.
- Focus: Full-body awareness. Identify where stress accumulates most.
- Modification: Shorten tense/release cycles if time-constrained.
Day 3: 4-7-8 Breathing
- Setup: Sit upright with hand on belly. Ensure quiet environment.
- Steps: Inhale deeply through nose for 4 seconds → hold breath for 7 seconds → exhale slowly through mouth for 8 seconds. Repeat cycle 5 times.
- Focus: Breath control. Feel diaphragm expansion/contraction.
- Modification: Reduce counts to 3-5-6 if lightheaded.
Day 4: 4-7-8 Breathing
- Setup: Maintain upright posture. Add candle flame visual focus point.
- Steps: Extend to 7 cycles. After final exhale, sit silently observing natural breath rhythm for 1 minute.
- Focus: Respiratory rhythm. Maintain smooth transitions between phases.
- Modification: Use whispered 'whoosh' sound during exhalations.
Day 5: Mindfulness Meditation
- Setup: Comfortable seated position. Set timer for 5 minutes.
- Steps: Focus on breath sensations. When thoughts arise, label them 'thinking' and gently return to breath. No judgment for distractions.
- Focus: Present-moment awareness. Notice how thoughts come and go like clouds.
- Modification: Use guided meditation audio if struggling.
Day 6: Mindfulness Meditation
- Setup: Same as Day 5. Add background white noise if preferred.
- Steps: Expand to 6 minutes. After 4 minutes, shift focus to ambient sounds for remaining time.
- Focus: Thought observation. Notice patterns without engagement.
- Modification: Count breaths 1-10 then restart if needed.
Day 7: Guided Meditation
- Setup: Choose comfortable position. Use headphones for immersion.
- Steps: Follow 7-minute guided session. Focus completely on instructor's voice and suggested imagery.
- Focus: Integrated practice. Combine breath, body scan, and mindfulness elements.
- Modification: Try different guide voices to find best fit.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Discomfort in meditation is perfectly normal, especially at the beginning of practice. The mind may switch from one thing to another continuously. But this is all right. Try walking meditation. Pay attention to the feeling of your feet touching the ground. Note the sensation in the bottoms of your feet. This exercise helps direct any nervous energy.
If racing thoughts interfere with your focus, then label them 'thinking' kindly. Return your attention to your breath anchor. For noisy locales, use nature sound recordings. The sounds of rain or ocean obscure the external distractions. If you live in a household that is constantly busy, earplugs can also be a great help. Tailor your practice to fit the environment.
Bodily discomfort generally puts beginners off. If your body hurts when you sit, try chair meditation. Have both feet flat on the floor. Have a cushion behind your lower back. Standing meditation is also an option. Shift the weight from one foot to the other. Find positions that feel sustainable to you.
Feeling an emotional surge indicates that this is working. Breathe during the discomfort. If you feel too overwhelmed, it is okay to temporarily shorten the practice time. You might want to try a few loving kindness phrases such as "may I be calm." These modifications help you continue practicing in a way that gradually builds your resilience.
Restlessness and Impatience
- Solution: Start with short 2-minute sessions. Use walking meditation technique: Focus on sensation of feet touching ground.
- Tip: Set gradual duration increases: Add 30 seconds every 3 days.
- Modification: Practice while doing routine tasks like washing dishes.
Racing Thoughts
- Solution: Label thoughts 'thinking' without judgment. Return to breath anchor.
- Tip: Try counting breaths 1-10 then restarting.
- Modification: Use guided meditations when thoughts overwhelm.
Physical Discomfort
- Solution: Adjust posture frequently. Use cushions for support.
- Tip: Try chair meditation with feet flat on floor.
- Modification: Lie down if seated position causes pain.
Falling Asleep
- Solution: Meditate upright with eyes slightly open. Practice earlier in day.
- Tip: Splash cool water on face before session.
- Modification: Use standing meditation posture.
Emotional Overwhelm
- Solution: Notice emotions without analysis. Visualize them as passing weather.
- Tip: Shift to loving-kindness meditation when distressed.
- Modification: Reduce session time during high-stress periods.
Long-Term Practice Power
Through neuroplasticity, your brain actually rewires itself with regular meditation. Neural pathways become reinforced, much like the muscles of your body do with exercise, so that, over time, the responses of calmness become automatic. You develop new connections that go around your old patterns of anxiety.
Build gradually the time of your sessions as practice deepens. Begin with five minutes a day and add one minute a week. Notice clearer thoughts. Your emotional balance has improved greatly. The physical tension is released more completely also. The longer the practice is maintained, the more marked will be this change.
Progress may not always be linear. Some days feel easy. Other days, your brain may be in constant motion. This is normal. Trust the cumulative effect. Each session builds resilience regardless of the results you feel immediately. Your brain is still changing behind the scenes.
Use regular brief sessions in your transformational program to keep up or renovate what has occurred, yet 20 minutes a day will maintain benefits. Use different methods to avoid stagnation. Take note of minor improvements monthly. This ongoing process helps keep your brain rewired to function properly in response to stress-producing stimuli.
Brain Structure Changes
- Fact: Regular meditation thickens the prefrontal cortex significantly. This brain region governs emotional regulation and decision-making.
- Fact: The amygdala reduces in size with consistent practice, lowering reactivity to anxiety triggers. Structural changes become established over time.
- Fact: Neural pathways strengthen between rational and emotional brain centers, improving anxiety response coordination.
Hormonal Balance
- Fact: Cortisol production decreases with ongoing practice. Lower stress hormones reduce physical anxiety symptoms.
- Fact: Melatonin regulation improves, enhancing sleep quality. Deeper sleep further supports emotional resilience.
- Fact: Serotonin sensitivity increases, creating natural mood stabilization without medication.
Autonomic Nervous System
- Fact: Resting heart rate decreases noticeably after consistent practice. This indicates improved cardiovascular efficiency.
- Fact: Heart rate variability increases significantly, showing better nervous system balance.
- Fact: Recovery time from stressful events improves faster with regular meditation practice.
Cognitive Benefits
- Fact: Attention span increases with mindfulness practice. Focus improvements help redirect attention from anxious thoughts.
- Fact: Working memory capacity expands, helping manage multiple stressors without overwhelm.
- Fact: Cognitive flexibility improves, enabling reframing of anxious thoughts into neutral perspectives.
Emotional Resilience
- Fact: Emotional reactivity to negative stimuli decreases with ongoing practice.
- Fact: Self-compassion increases noticeably, reducing self-criticism that fuels anxiety.
- Fact: Baseline mood elevation occurs without external triggers after consistent meditation.
5 Common Myths
All thoughts need to be erased to effectively meditate, otherwise it will not work.
Meditation does not require the erasure of thoughts but the noticing of thoughts without judgement. When one becomes distracted with a thought of worry of thoughts of plans, to gently realize them and return to concentration upon the breath is the doing of it. This recognition of distraction and the repatterning of concentration permits the refining of focus to be cultivated, making the practice beneficial in the long run.
For significant benefits on anxiety, mediation requires hours of practice each day.
Great benefits in anxiety reduction can be achieved by consistently practicing short sessions and not by marathon practices of mediation. The practice of mediation daily for brief periods can produce in a few weeks reduced stress hormone levels and improved regulation of emotions. The key is not in duration of the practices but rather their daily consistancy. Short but daily practice are more efficient in producing positive changes than occasionally long periods of practices.
Meditation is intrinsically connected to religion or spirituality, and therefore is a contradiction to a secular lifestyle.
The newest methods of meditation are thoroughly secular and practical, requiring no spiritual belief. Awareness of the breath, body scans etc., relate only to physiological and psychological processes. These methods are taught in many places without any reference to religion whatsoever. It is the regularity of practice which produces the results, not the beliefs and doctrines.
Experiencing anxiety during meditation means you're failing at the practice or doing it incorrectly.
Anxiety surfacing during meditation indicates the practice is working as intended. As you create mental space, worries naturally surface for processing. Noticing anxious thoughts without reaction builds emotional resilience. This temporary discomfort is part of developing new response patterns to stress.
You should experience immediate anxiety relief from meditation after just one or two sessions.
Like physical exercise, meditation produces its results gradually, through persistence. While you may have a feeling of calmness after a session, the alleviation of anxiety is gradual as the body adjusts. Most practitioners can see results after several weeks of daily practice, regularly applied.
Conclusion
Meditation is an easy way to access a physiological solution to alleviate anxiety. It interacts directly with the body's stress response system. No special equipment is required for this natural method. You can practice it anywhere, any time. It effectively rewires the brain's reaction to stressors.
Emphasize consistency, not perfection. Short daily sessions yield lasting results. Days will be missed. Resume your practice. Consistent effort builds resilience rather than perfect execution. This is how meditation becomes sustainable for real-life challenges.
Observe how somatic changes encourage emotional freedom. Your heart rate will decrease automatically, and your breathing will slow and deepen. These physiological changes will bring space into your mind and help you distance yourself from anxious thoughts. As a result of the physiological changes, you can maintain an emotional foundation that lasts.
Begin your daily practice today. Devote just five minutes every morning. Find a comfortable sitting position. Notice your breath. This intentional practice will start changing the way you relate to anxiety instantly. Your journey towards calm begins now.
External Sources
Frequently Asked Questions
What meditation techniques work best for anxiety?
Mindfulness meditation and focused breathing exercises are most effective for anxiety. These techniques physically calm the nervous system by reducing cortisol and slowing heart rate. Regular practice rewires brain pathways for better stress response.
Can meditation cure anxiety permanently?
Meditation significantly manages anxiety symptoms through consistent practice, but requires ongoing maintenance like physical fitness. It creates lasting neurological changes that reduce reactivity to triggers, providing sustainable relief when practiced regularly.
How quickly can I expect anxiety relief?
Noticeable anxiety reduction typically begins within several weeks of daily practice. The timeline varies based on:
- Consistency of practice
- Technique selection
- Individual physiology
- Baseline anxiety levels
Why might meditation initially increase anxiety?
Temporary anxiety spikes occur as suppressed emotions surface during early practice. This actually indicates the process is working - your mind is learning to process rather than avoid feelings. Persist through this adjustment phase for long-term benefits.
What natural approaches complement meditation?
Combine meditation with these anxiety-reducing practices:
- Regular physical exercise
- Consistent sleep patterns
- Balanced nutrition
- Mindful caffeine reduction
- Nature exposure
How long should meditation sessions last?
Begin with brief five-minute sessions, gradually extending to fifteen-twenty minutes daily. Consistency matters more than duration - regular short practices build neurological changes more effectively than occasional long sessions.
Can meditation replace anxiety medication?
Meditation complements but shouldn't replace prescribed medication without medical consultation. It works synergistically with treatments by enhancing emotional regulation. Many practitioners eventually reduce medication under professional supervision as meditation skills develop.
What if I can't stop thoughts during meditation?
The goal isn't thought elimination but changing your relationship with thoughts. Strategies include:
- Gently returning focus to breath
- Labeling thoughts as 'thinking'
- Observing thoughts without judgment
- Using guided meditations initially
Is meditation effective for severe anxiety?
Meditation benefits all anxiety levels, though severe cases should combine it with professional support. It physically reduces amygdala reactivity while strengthening prefrontal cortex regulation, creating measurable physiological changes even in clinical anxiety.
How does meditation physically reduce anxiety?
Meditation creates tangible physiological changes:
- Reduces stress hormone production
- Slows resting heart rate
- Improves heart rate variability
- Decreases amygdala activation
- Thickens prefrontal cortex

